![]() Views: 1,015
Views: 1,015
A Complete Guide For Adenoidectomy
Dedicated Support at Every Step!
Our Doctors are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week to help you!
Table of Contents
What is adenoidectomy?
No Cost EMI, Hassle-free Insurance Approval
What is adenoiditis?
Adenoiditis refers to the infection and inflammation of the adenoid glands. The most common causes of adenoiditis include infection (bacterial or viral) and allergies.
The adenoid glands are lumps of lymphoid cells located on the roof of the mouth, just behind the nose. They are a part of the immune system and help protect the body from viral and bacterial infection, especially in kids.
However, as a child grows, the adenoids start shrinking. Adenoids start shrinking around the age of 5 to 7, and they can completely disappear by the teenage years.
When does an adenoidectomy become necessary?
Surgery is usually considered inevitable when the symptoms of adenoiditis become serious and can no longer be managed with just medicines.
When the adenoids swell up and increase in size, they, partially or completely, block the airway. This can lead to various complications such as breathing problems, ear infections, snoring, etc. If left untreated, these complications can worsen and lead to serious breathing difficulties such as sleep apnea, chronic sinus infections, etc.
Also Read: 10 Home Remedies For To Cure Swollen Adenoids Naturally
Sleep apnea is a condition in which the person stops breathing while sleeping at night. It can be very dangerous, especially for children. It can also lead to chronic nasal drainage congestion and sinus infections, along with severe ear infections, which can even lead to temporary loss of hearing.
Adenoidectomies are usually recommended if:
- The patient has chronic ear/sinus infections that are not responding to medical treatments.
- The patient is experiencing bouts of adenoiditis over 5-6 times a year.
- Pain and inflammation from adenoiditis are interfering with their lives.
Adenoidectomy in children
Since adenoiditis most commonly occurs in children, its initial symptoms are often overlooked or confused with other diseases. To make the diagnosis and treatment for adenoiditis easier, it is important that parents educate themselves better about this condition.
Look for symptoms such as mouth breathing, loud snoring, frequent sore throat, sinus infections, etc., in your child. If your child is having trouble breathing at night, then that is a big sign that he may have adenoiditis.
Adenoidectomy surgery may sound scary, especially in children, however, it is a very safe procedure. Since there is no open incision, there are no sutures and only minimal scarring. Recovery is especially fast in children and they can return to their daily lives within a week of the surgery.
In children, adenoidectomy offers a variety of benefits such as improved breathing, along with fewer throat, ear, and sinus infections.
What are the indications and contraindications of adenoidectomy surgery?
| Indications | Contraindications |
| Airway obstruction and breathing difficulties | Palatal insufficiency, i.e., cleft palate |
| Recurrent or persistent ear infections | Bleeding disorders |
| Recurrent or persistent sinus infections | Active infection |
How to prepare for an adenoidectomy?
The first thing your surgeon will do is collect your medical and family history. If you are aware of any allergies or bleeding/clotting disorders that you may be prone to, you should tell your doctor at this time, so that they can alter the procedure to suit your needs.
In the week before the surgery, avoid medicines such as ibuprofen and aspirin as they affect the blood clotting. Do not self-medicate. If you are in any pain or discomfort, discuss it with your doctor before starting any medicine.
Since you need to have an empty stomach during the surgery, you may be advised to avoid all food intake, including water, after midnight on the day of the surgery.

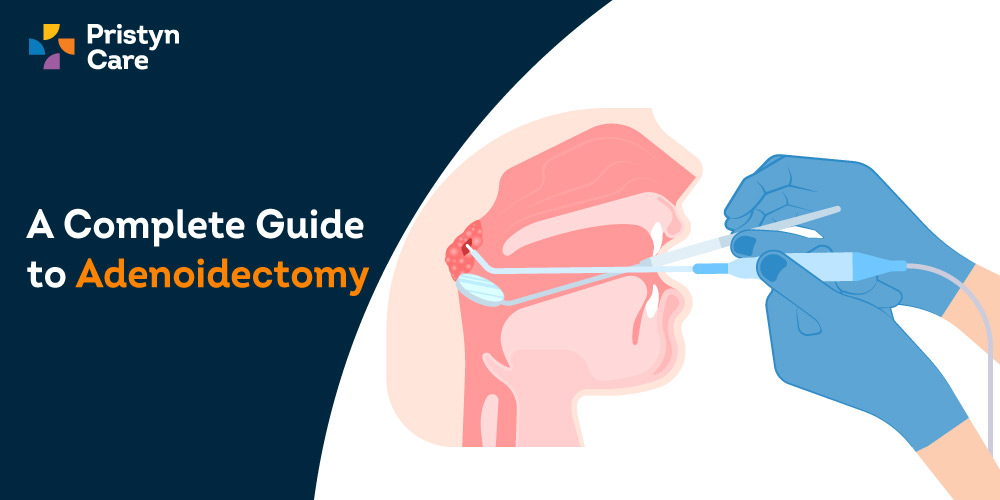
How is adenoidectomy performed?
Adenoidectomy is a short and straightforward procedure. Normally, it is a very safe procedure and is not associated with any severe complications. The procedure can be performed under either local or general anesthesia, but for children, general anesthesia is preferred.
The surgeon holds the child’s mouth open using a retractor and removes the adenoids using a spoon-shaped device (curette), electric device, or laser. Then the incision is sealed off using an electric cauterizer or packed with absorbent gauze to limit the bleeding. Once that is done, the patient is moved to a recovery room.
The entire surgery takes about 20-30 minutes to complete. It can be performed as a daycare procedure, but usually, patients are hospitalized overnight to make sure there are no complications.
How to improve recovery after an adenoidectomy?
After the surgery, most patients experience mild discomfort and pain, including sore throat, runny nose, noisy breathing, bad breath, etc. These symptoms often resolve on their own within a couple of weeks after the surgery. Recovery is much faster in kids and they can return to their daily lives within a week.
You can also improve your recovery by following the given tips:
- Take pain medication, as prescribed by your ENT doctor.
- Use ice cubes to gently massage the area to help relieve swelling in the area.
- Hydrate yourself well. You can drink plenty of liquids such as water, fruit juice, gatorade, Jell-O, apple sauce, warm chicken or beef broth, etc.
- If you are unable to swallow anything after the surgery, you can start with a liquid diet or soft foods, such as pudding, soup, gelatin, mashed potatoes, yogurt, boiled vegetables, etc.
- Avoid hot and spicy foods as they may irritate your throat and the surgical area. You should consume cold liquids and desserts such as soft-serve ice cream during this period.
- Rest well. Do not put any strain on your throat and associated areas till you have recovered. Do not blow your nose or play rough/contact sports in your recovery period.
- Use a humidifier if necessary. It will prevent allergies and help you breathe better.
- Do not travel by airplane for a couple of weeks after the surgery as altitude change can adversely impact the recovery.
What should I expect after adenoidectomy surgery?
Though a little pain and discomfort are ok, you should immediately contact your ENT surgeon if you have a high fever, uncontrolled vomiting, etc., as these are signs of severe complications and should be managed immediately.
A mild fever along with an upset stomach and vomiting are very common for the first 24-48 hours after the surgery, however, if the vomiting persists beyond that, then it needs medical management.
Other things you must look out for include epistaxis (nose bleeds), blood or discharge from the surgical area, signs of dehydration (sunken eyes, dry and sticky lips, no urine for over 8 hours, and no tears), etc.
What are the risks associated with adenoidectomy?
Although very rare, in some cases, adenoidectomy can lead to a few complications such as:
- Failure to relieve symptoms, such as breathing problems, ear and sinus infections
- Uncontrolled hemorrhage
- Permanent change in the vocal performance
- Infections
- Anesthetic complications
Before the surgery, you should ask your surgeon about all these complications and their management to be completely prepared for the surgery.
Does adenoidectomy weaken the immune system?
No, adenoids amount to a very small part of the immune system. Several research studies have revealed that adenoidectomy does not make anyone more prone to infections or diseases, whether the patient is a child or an adult. This is because the immune system has many different ways to identify and fight infections. In fact, in many cases, by preventing recurrent ear and sinus infections, adenoidectomy strengthens the immune system.
What is T&A surgery?
T&A surgery stands for tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy surgery, or adenotonsillectomy. In this surgery, both tonsils and adenoids are removed at the same time. Both tonsillitis and adenoiditis often lend to each other, i.e., infection of one leads to infection of the other. Hence, it is commonly performed in patients who have recurring tonsil and adenoid infections.
The procedure and recovery for T&A are essentially the same as it is for adenoidectomy. Most patients who are undergoing adenoidectomy often undergo tonsillectomy at the same time to prevent recurrence of the infection and improve breathing at the same time.