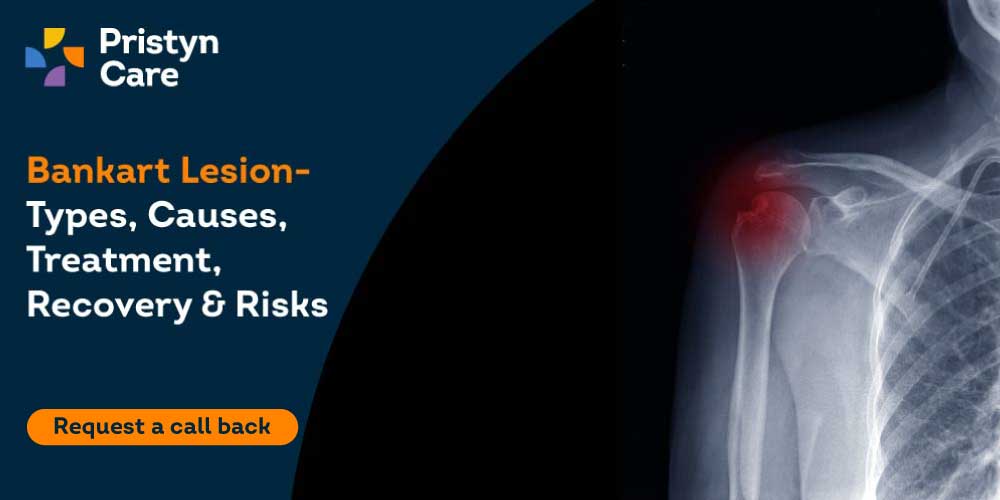
A bankart lesion is a lesion of the anterior part of the glenoid labrum, i.e., the fibrocartilagenous rim of the margin of the shoulder blade. The most common cause for bankart lesions is repeated anterior dislocation of the shoulder joint. It is very common in athletes, especially volleyball, tennis, and handball players.
Table of Contents
Anatomy of the shoulder joint
The shoulder joint is one of the largest and most complex joints in the body. It is a ball and socket joint that is formed by the humerus (ball) fitting inside the scapula (socket). The shoulder movements are largely managed and controlled by the glenoid labrum. The dislocation of the shoulder joint anteriorly causes damage to this glenoid labrum. Damage to the labrum cartilage leads to instability of the joint, which in turn leads to repeated dislocation of the shoulder joint.
How are bankart lesions caused?
The shoulder joint is designed to provide maximum mobility to the arm, and in order to achieve that, its stability is sacrificed. The glenohumeral joint (shoulder) joint is the most unstable and hence, the most frequently dislocated joint in the human body.
The most common type of dislocation occurring in the shoulder joint is anterior shoulder instability, which mostly occurs during the abduction, extension, and external rotation movements. As the instability and the number of dislocations increase, it leads to tearing of the glenoid labrum, also known as bankart lesion.
Although rare, if the shoulder joint gets dislocated posteriorly, it can lead to a reverse bankart lesion.
The most common cause for a bankart lesion is repeated shoulder dislocation due to a trauma or a sports injury. Bankart lesions can be caused by:
- Sports collisions
- Overuse of the shoulder joint
- Repeated abduction, extension, and external rotation movements of the shoulder joint
- Car accidents
- Awkward landing while falling down from a ladder or stairs
- Loose shoulder ligaments
If you have suffering from chronic shoulder pain, shoulder dislocation or any other condition related to the bones and joints, you should consult an orthopedic specialist for appropriate treatment. You can consult the best orthopedic doctor in your city at your nearest Pristyn Care clinic.
What are the types of bankart lesions?
There are two types of bankart lesions:
- Soft tissue bankart lesions: It occurs when the damage occurs in the glenoid rim, i.e., when the posterior capsule is stretched, the inferior glenohumeral ligament is being torn.
- Bony bankart lesions: A bony bankart lesion basically means that there is a fracture of the glenoid rim in addition to the soft tissue damage.
What are the symptoms of a bankart lesion?
The most common symptoms of a bankart lesion are shoulder weakness and instability, along with repeated shoulder dislocation. In addition to that, bankart lesions are characterized by generalized shoulder pain that gets worse when the arm is held in the back.
Other symptoms of bankart lesions include swelling, numbness, and bruising of the shoulder joint. Sometimes, there may be muscle spasms and tingling sensations in the neck and down the arm.
Bankart lesions often present with similar symptoms to rotator cuff tears and SLAP lesions. Hence, it is important to perform a thorough diagnosis is performed to ensure that proper treatment is being administered.
What are the diagnostic procedures performed for bankart lesion diagnosis?
Bankart lesions often occur in conjunction with shoulder dislocations, but they are hard to diagnose with just a physical examination. For the diagnosis of a bankart lesion, a soft tissue imaging test such as an MRI scan is required. An MRI provides an accurate picture of the soft tissues and helps identify any tears in the glenoid cartilage.
Other diagnostic tests that can be performed to accurately diagnose a soft tissue bankart lesion include arthroscopy and MR arthrography. On the other hand, a bony bankart lesion can be easily diagnosed through radiographs.
How are bankart lesions treated?
Conservative management
Conservative management for bankart lesions is performed by rest, immobilization, and physical therapy. The joint is immobilized to prevent further damage to the muscles, veins, and nerves in the shoulder joint. Physical therapy is provided for at least 3-4 months to restore the range of motion of the joints, strengthen the muscles and cartilages supporting it and prevent future dislocations in the joint.
It is generally preferred for older patients who are contraindicated for surgical treatment due to poor health or immune condition.
Conservative nonoperative treatment for bankart lesions is generally not recommended to most patients as it has a recurrence rate of about 17-96%, even in patients under 30 years of age.
Surgical Repair
During surgery for bankart repair, the surgeon uses screws called anchors to re-attach the torn/worn out shoulder ligaments to their proper position.
Open surgery
In open bankart repair surgery, the surgeon makes an incision in the front of the shoulder to repair damaged cartilages and ligaments. It is usually performed for patients who have severe shoulder instability or patients who have had an unsuccessful bankart repair surgery in the past.
Arthroscopic surgery
During arthroscopic surgery, the surgeon creates a few tiny incisions on the shoulder joint to perform the surgery. It is the most common and effective bankart repair procedure.
Arthroscopic bankart repair provides a faster recovery time but the recurrence rate is lower for open bankart surgery.
Cities where we offer Bankart Repair and Shoulder Dislocation Treatment
What are the risks of untreated bankart lesions?
If left untreated over a long time, bankart lesions can cause chronic shoulder instability, characterized by extreme pain and stiffness in the shoulder joint. Over time, the joint will become completely unstable and immobile. Even if you force movement in the joint, it will lead to joint dislocation.
It can even lead to the development of degenerative musculoskeletal diseases such as osteoarthritis, adhesive capsulitis, etc. in the affected joint.
What happens after bankart surgery?
After bankart surgery, proper rehabilitation and physical therapy are required to restore complete joint mobility and increase muscle strength. While performing shoulder physiotherapy, there are 7 key factors to be considered such as:
- Cause of the shoulder pathology
- Degree of shoulder instability
- Frequency of shoulder dislocation
- The direction of shoulder instability (anterior, posterior, multidirectional)
- Patient’s general health condition
- Activity level and requirements from the shoulder joint
- End range neuromuscular control of the joint
Phases of rehabilitation after surgery
Usually, rehabilitation after bankart surgery is divided into three stages:
First phase: The first phase of rehabilitation is sling immobilization. It lasts for about 4 weeks and allows for a limited range of motion, i.e., 20o of abduction and 40o of internal rotation. During this phase, only muscle strengthening exercises are performed.
Second phase: During this phase, patients perform active-assisted range of motion exercises to improve the passive range of motion of the joint. The duration of this phase is dependent on the improvement in the patient’s joint motion.
Third phase: The third phase is basically achieved when the patient has regained a complete range of motion and the patient can return to their normal life.
What are the risks associated with bankart shoulder repair?
- Recurrent shoulder instability and stiffness
- Hemorrhage
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Blood vessel or nerve injury
- Post-traumatic arthritis
Conclusion
The most common sign of bankart repair is chronic shoulder pain and stiffness. Ignoring these signs can lead to damage to the neuromuscular tissues surrounding the joint. Even a single joint dislocation can lead to further joint instability that may remain undiagnosed for a long time if proper diagnostic tests are not performed.
If you have any signs of shoulder tear such as repeated shoulder dislocation, pain, etc., book an appointment with the best orthopedic doctor near you for an expert consultation.







