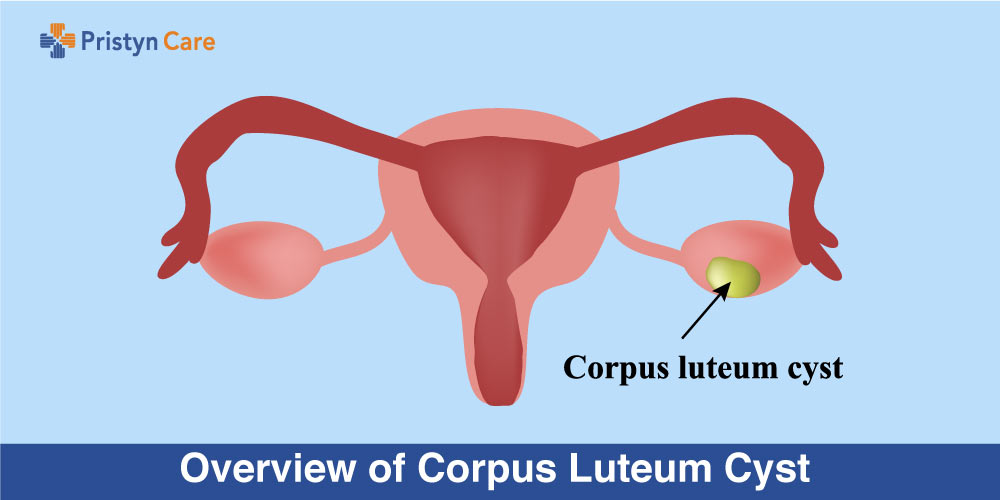
Corpus luteum cysts are a type of a functional ovarian cyst that occurs when a corpus luteum fails to relapse following the release of an ovum. When linked with pregnancy, it is the most common pelvic mass encountered in the first trimester. At times, the corpus luteum can accumulate with fluid. The buildup and accumulation of fluid can cause a corpus luteum cyst.
In most cases, corpus luteum cysts go away on their own without specified treatment. Corpus luteum cysts may disappear on its own in a few weeks or may take up to 3 menstrual cycles to vanish.
Some females who develop corpus luteal cysts may experience one or more of the following symptoms-
- Pelvic pain, which may be dull or sharp
- Abdominal fullness or heaviness
- Bloating
- Pain in the lower back and thighs
- Painful sex
- Unexplained weight gain
- Painful menstrual cycle
- Breast tenderness
- Frequent need to urinate
- Difficulty emptying bladder and bowels completely
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
Some females may experience a burst cyst, which can lead to severe pain and possibly internal bleeding. Larger corpus luteum cysts can cause the ovary to twist on itself (known as ovarian torsion) which can severely affect the blood flow to the affected ovary.
At times, the corpus luteum cyst may remain even after the early stages of pregnancy. In such cases, the cyst has the potential to give rise to grave problems. An obstetrician will help you monitor as appropriate and suggest the best treatment option to prevent any complications.
Also Read- What To Do In Case The Ovarian Cyst Rupture?
Table of Contents
Who is at a risk of Corpus Luteum Cysts?

Any female can get corpus luteal cysts, though they are more likely to occur in females taking medication to induce ovulation. Such medications are usually prescribed by a doctor or a gynecologist for females with PCOS or those who are experiencing fertility problems.
It is essential to note that as the corpus luteum is a normal part of the period cycle, the type of functional ovarian cyst linked to them can also develop when a female is not pregnant. A female can also develop corpus luteal cysts even if she is not taking, or has never taken medication for fertility. If a female has had a corpus luteal cyst in her pregnancy it does not necessarily mean that she will have one in her next pregnancy as well.
Also Read: Is Pregnancy Possible with PCOS?
Symptoms of corpus luteal cyst

Some females notice one-sided pain during their period cycle. The pain may be worrisome, especially if the female is sexually active and concerned about the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy. This may prompt a visit to your gynecologist.
But in many cases, females who have a corpus luteal cyst do not notice any pain and may not even realize they have developed the cyst. As corpus luteal cyst typically resolves on its own, most females do not even realize it was ever there.
Diagnosis
Corpus luteal cysts are diagnosed with an ultrasound. However, the ultrasound may be different from the one most females expect. These cysts tend to be easier to see with an internal, or a transvaginal ultrasound.
Treatment and Complications

A corpus luteal cyst is usually not a call for concern. They do not typically cause any major symptoms or complications during pregnancy, especially when the cysts are discovered in the first trimester.
If the cyst causes pain, the doctor may prescribe pelvic rest or pain medications to the female for relief. In most cases, corpus luteal cysts resolve on its own.
Occasionally the cyst may get rupture. The pain may increase but subside quickly if the cyst ruptures. The doctor may prescribe pain medication and advise the female to take bed rest if anything so happens.
Less frequently, a corpus luteal cyst can cause the ovary to twist (known as torsion). It can be very painful for the female and may require surgery to prevent further injury of the ovaries
Final Words
The doctor may suggest the female to have another ultrasound to check on the corpus luteal cyst if the female continues to have symptoms. Otherwise, unless treatment is required, the female does not need follow-ups. Consult the best gynecologist for corpus luteal cyst at your nearest Pristyn Care clinic.
Also Read: