Eczema and psoriasis are two of the most common chronic skin conditions affecting millions worldwide. Although they often look alike, their underlying causes, symptoms, and treatments differ significantly. Knowing how to identify and manage each condition is key to improving quality of life and avoiding unnecessary suffering.
In this guide, we will take you through everything you need to know — from recognising symptoms to choosing the right eczema treatment or planning effective psoriasis treatment.
Table of Contents
What is Eczema?
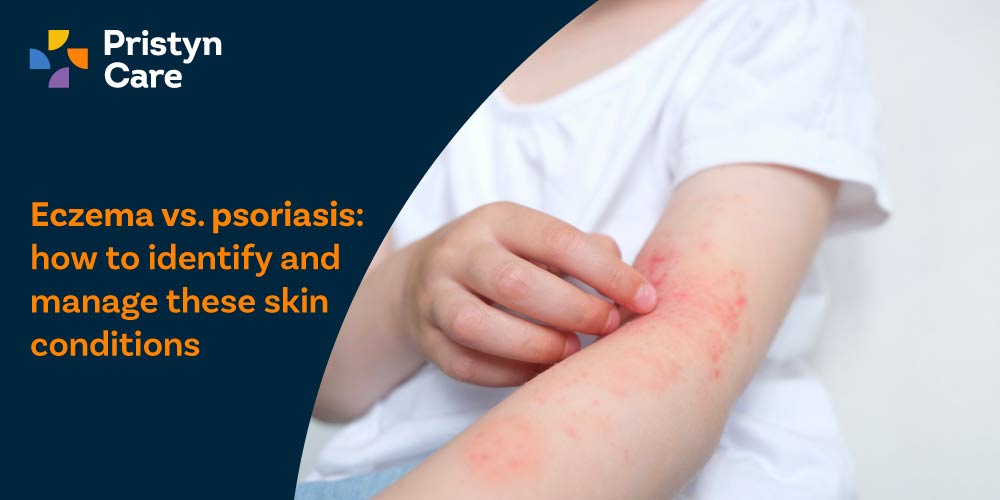
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterised by red, dry, and itchy patches, which may sometimes blister or ooze. While not contagious, it can be persistent and often has a genetic component.
There are several types of eczema, each with distinct triggers and patterns. The condition can affect both children and adults, with flare-ups occurring at any time, particularly in response to allergens or environmental irritants
Key Features of Eczema:
- Dry, flaky skin that may crack or bleed: These areas often appear on hands, face, neck, elbows, and behind knees, especially during colder months or in dry environments.
- Severe itching that leads to scratching and worsens the rash: Scratching can cause more inflammation, and sometimes result in thickened skin or infection.
- Red, inflamed patches or weeping blisters: These may ooze fluid and eventually crust over, particularly in the acute phase of eczema.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that causes skin cells to regenerate too quickly, leading to thick, scaly patches. It is a lifelong condition that varies in severity and often follows a cycle of flare-ups lasting weeks or months, followed by periods of remission.
There are several types of psoriasis, each affecting different areas of the body in distinct ways.
Key Features of Psoriasis:
- Red patches of skin with silvery-white scales: These plaques commonly appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back but can develop anywhere on the body.
- Thickened skin that may crack or bleed: Rapid skin cell turnover leads to dryness and rigidity, making the skin prone to painful fissures.
- Burning or soreness in affected areas: Unlike eczema, psoriasis often causes a stinging or burning sensation rather than intense itching.
Eczema Vs Psoriasis: Comparison Table
While eczema and psoriasis can look similar at first, their causes and behaviours are quite distinct. This detailed comparison highlights the differences for better understanding and diagnosis.
| Feature | Eczema | Psoriasis |
| Cause | Triggered by irritants, allergens, or environmental factors; immune system overactivity | Autoimmune disorder causing rapid skin cell production |
| Appearance | Red, inflamed skin often with oozing or crusting; texture is rough and dry | Raised, thickened plaques with silvery scales; skin feels tight and rigid |
| Itching | Often intense and unrelenting; worsens at night | Present but usually milder than eczema; may feel like burning or stinging |
| Common Areas | Bends of arms and knees, neck, face, hands | Elbows, knees, scalp, lower back |
| Age Group | Common in infants and young children but can affect adults | Common onset between ages 15 and 35; can also appear later |
| Flare Triggers | Soaps, allergens, temperature, stress, clothing | Infections, injury to skin, medications, stress |
| Infectious? | No | No |
| Related to other conditions? | Often associated with asthma or hay fever | Associated with psoriatic arthritis in some patients |
Symptoms of Eczema and Psoriasis
Symptoms may overlap, but there are subtle clues that help differentiate the two. Recognising the specific symptoms can help guide diagnosis and inform effective eczema treatment or psoriasis treatment.
Eczema Symptoms:
- Extreme itching that starts before the rash appears: Often the earliest sign, itching can become unbearable and is worse at night.
- Red or brown patches that may crust or weep fluid: These lesions often appear on the hands, wrists, feet, ankles, or chest.
- Skin thickening from chronic scratching: This leads to leathery skin, especially in persistent or untreated cases.
Psoriasis Symptoms:
- Silvery, scaly plaques with sharply defined borders: These plaques are typically dry, thick, and appear in consistent locations.
- Pain or soreness around affected areas: Psoriasis can cause discomfort even without scratching due to inflammation.
- Pitting or discolouration of nails: A hallmark symptom of psoriasis not found in eczema.
Causes and Risk Factors
Both eczema and psoriasis are influenced by genetics and the immune system, but their triggers and underlying mechanisms differ.
Eczema Causes:
- Genetic predisposition and a faulty skin barrier: The skin is unable to retain moisture, leading to dryness and sensitivity to irritants.
- Overreaction of the immune system to allergens: This results in inflammation and the development of skin rash symptoms.
- Environmental triggers like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander: Exposure to these can cause flare-ups and itching.
Psoriasis Causes:
- Autoimmune activity that accelerates skin cell growth: The body mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, resulting in buildup and plaques.
- Family history of psoriasis or autoimmune diseases: A major risk factor, especially if one or both parents have the condition.
- External triggers like infections, cold weather, and stress: These factors can cause the immune system to become overactive.
Types of Eczema (Eczema Types)
There are several eczema types, each presenting with slightly different symptoms and triggers. Understanding these distinctions helps guide targeted eczema treatment strategies.
Common Eczema Types:
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common form, linked with other allergic conditions such as asthma and hay fever.
- Contact Dermatitis: Caused by direct contact with irritants or allergens, such as cleaning products or certain fabrics.
- Nummular Eczema: Characterised by round, coin-shaped spots that can be extremely itchy and often ooze fluid.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Involves small, itchy blisters on the edges of fingers, toes, palms, and soles.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Affects oily areas like the scalp and face, often appearing as stubborn dandruff or flaky patches.
Variants of Psoriasis (Psoriasis Skin Disease)
Psoriasis skin disease presents in several clinical forms, each requiring specific treatment considerations. Identifying the correct type is crucial for effective psoriasis treatment.
Psoriasis Types:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common type, featuring thick red patches covered with silvery scales.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Small, red, dot-like lesions often triggered by infections such as strep throat.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Smooth, shiny lesions found in skin folds, such as under the breasts or in the groin.
- Pustular Psoriasis: White pustules surrounded by red skin, typically appearing on the hands and feet.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe form causing widespread redness, scaling, and extreme discomfort.
Diagnosing Eczema and Psoriasis
Proper diagnosis is essential to avoid mismanagement and to guide eczema treatment or psoriasis treatment plans.
Diagnosis Process:
- Clinical examination by a dermatologist: A visual inspection is often enough for experienced clinicians to distinguish the conditions.
- Patient history including triggers and flare-up patterns: A thorough review can reveal familial trends and identify environmental triggers.
- Skin biopsy in uncertain cases: A small skin sample may be taken for lab analysis to confirm the diagnosis.
Eczema Treatment: What Works Best?
Effective eczema treatment is diverse, targeting inflammation, dryness, and triggers. Treatment often includes both medication and lifestyle changes.
Eczema Treatment Strategies:
- Topical corticosteroids to reduce redness and inflammation: These are the mainstay of flare-up control and should be applied as directed.
- Regular use of moisturising agents and emollients: Keeping the skin hydrated prevents cracking and reduces itchiness.
- Avoidance of known triggers, such as soaps or fabrics: Lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce flare frequency and severity.
Psoriasis Treatment: Effective Approaches
Psoriasis treatment depends on the severity of the disease, the location of plaques, and how well the patient responds to different therapies.
Psoriasis Treatment Options:
- Topical medications like corticosteroids and coal tar: Useful for mild to moderate cases, particularly on the limbs or torso.
- Phototherapy with UVB light: Controlled exposure to UVB light slows skin cell growth and reduces scaling.
- Systemic medications and biologics for severe cases: These include drugs like methotrexate or biologic injectables that target the immune system directly.
Daily Life Impact: Eczema Vs Psoriasis
Both eczema and psoriasis affect more than just the skin. They can influence confidence, sleep, work, and even relationships. Let’s compare how each condition affects everyday life in unique ways.
Living with Eczema
- Interrupted sleep from intense itching: Night-time flare-ups cause discomfort that can disrupt rest, especially without regular use of moisturisers or the right eczema cream.
- Impact on clothing choices: Eczema-prone skin often reacts to rough fabrics, making sufferers avoid wool or tight-fitting clothes.
- Self-consciousness due to visible rashes: Embarrassment about an active skin rash may affect social interactions or cause anxiety.
- Time-consuming care routines: Applying creams multiple times daily can be demanding.
Living with Psoriasis
- Pain and bleeding from cracked plaques: Especially in psoriasis skin disease, plaques may split and cause discomfort during movement.
- Worry over flakes and visibility: Scalp psoriasis leads to flaking that can resemble dandruff, causing stress or self-consciousness in public.
- Stigma and misconceptions: Some wrongly believe psoriasis is contagious, which can lead to social awkwardness.
- Emotional toll: Flare-ups can trigger low mood or depression, especially when psoriasis treatment takes time to show results.
Final Thoughts
Although eczema and psoriasis may appear similar, they are distinct skin conditions with different causes, symptoms, and treatments. Whether you are experiencing a recurring skin rash, persistent itching, or painful plaques, effective management starts with an accurate diagnosis.
By using the appropriate treatments, understanding the different types of eczema, and staying informed about psoriasis, you can take control of your skin health and improve your quality of life.







