![]() Views: 1,753
Views: 1,753
Gynaecomastia vs Chest Fat
Understanding these differences is crucial as it not only enables effective treatment but also helps in addressing the psychological impacts they can have on self-esteem and body image.
Dedicated Support at Every Step!
Our Doctors are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week to help you!
Through this article, we aim to provide a clear understanding of gynaecomastia and chest fat, their causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and psychological effects.
Table of Contents
Understanding Gynaecomastia
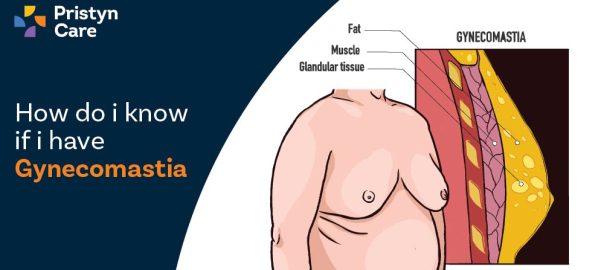
Gynaecomastia is a medical condition defined by the enlargement of breast tissue in males, seen commonly during puberty due to hormonal fluctuations. The main cause of gynaecomastia is an imbalance in levels of testosterone and oestrogen; specifically, increased oestrogen or decreased testosterone can lead to the development of glandular tissue in the breasts.
The symptoms of gynaecomastia include swollen breast tissue, sensitivity or tenderness in the chest area, and sometimes asymmetrical breast development. The texture of the affected area may feel firm or rubbery due to the presence of glandular tissue beneath the skin. In certain situations, gynaecomastia may be accompanied by pain or discomfort, especially when pressure is applied to the area.
This condition can stem from various causes beyond hormonal changes. Some medications like anabolic steroids or health conditions such as liver or kidney disease can also lead to gynaecomastia. Lifestyle factors like obesity can exacerbate hormonal imbalances. While gynaecomastia might not pose physical harm typically, it can inflict significant emotional distress and affect a person's self-image.
No Cost EMI, Hassle-free Insurance Approval
Understanding Chest Fat
When we talk about chest fat, we're referring to the build-up of adipose tissue in the chest area. This tends to give the chest a softer and fuller appearance. It is important to note that this is different from gynaecomastia, which involves an increase in glandular tissue rather than fat.
Chest fat is often linked to overall body weight and the way fat is distributed throughout the body. The biggest contributors to chest fat include factors like a poor diet, a lack of physical activity, or even a genetic tendency to store fat in a particular part of the body.
If you have excess chest fat, your chest may look a bit more rounded or full, but you will not typically experience pain or tenderness. The texture of chest fat is also generally soft and flabby as opposed to firm or rubbery. For some men, this could lead to feelings of insecurity about their body image, although it is usually less emotionally distressing than gynaecomastia.
Distinguishing Gynaecomastia from Chest Fat
It is important to distinguish between gynaecomastia and chest fat, as these two causes of male breast enlargement have different characteristics and treatment approaches.
Physical Examination
One of the fundamental ways to distinguish between gynaecomastia and chest fat is through a physical examination. In this process, a doctor will assess the texture and firmness of your breast tissue. For instance, glandular tissue associated with gynaecomastia tends to be firm and may feel lumpy or rubbery beneath the nipple area. On the other hand, chest fat will likely feel softer and more spread out across the chest without any specific areas of firmness.
In addition, gynaecomastia can sometimes lead to uneven breast development, where one side appears larger than the other. Chest fat, however, typically results in a more uniform distribution across both sides. If you're experiencing tenderness or pain in the breast area, this could be an indication of gynaecomastia rather than just the accumulation of fat.
Medical Tests
Sometimes, further medical tests are required to confirm whether it's gynaecomastia or chest fat. These can include blood tests to check hormone levels, specifically testosterone and oestrogen. Other diagnostic tools like mammograms or ultrasounds may also be used to evaluate the composition of your breast tissue.
Through blood tests, doctors can identify if there are any underlying hormonal imbalances that could be contributing to gynaecomastia. Meanwhile, imaging studies can provide visual evidence of whether the tissue in your chest is primarily glandular or fatty.
By understanding these diagnostic methods, it becomes easier to accurately differentiate between gynaecomastia and chest fat. This, in turn, guides the appropriate treatment strategies for each condition.
MBBS, MS-General Surgery, M.Ch-Plastic Surgery, DNB-Plastic Surgery
₹2000₹1000Consultation Fee
M.B.B.S, M.S. (General Surgery), M.Ch. (Plastic Surgery), DrNB (Plastic Surgery)
₹2000₹1000Consultation Fee
MBBS, MS - General Surgery, M.Ch. - Plastic Surgery
₹2000₹1000Consultation Fee
MBBS, M.S.(Gen. Surgery), DNB (Gen. Surgery), F.MAS, D.MAS, FAIS, FALS, FIAGES
₹2000₹600Consultation Fee
Dr. Balasundaram Kutty Alalasundaram
MBBS, DNB-General Surgery, M.Ch- Plastic Surgery
₹2000₹600Consultation Fee
MBBS, DNB-General Surgery, DNB-Plastic Surgery
₹2000₹600Consultation Fee
Dr. Bhagyashri Bhalchandra Talele
MBBS, MS-General Surgery, M.Ch-Plastic Surgeon
₹2000₹600Consultation Fee
Treatment Options for Gynaecomastia and Chest Fat
Treatment options for gynecomastia and chest fat vary widely, encompassing both non-surgical and surgical interventions tailored to the underlying causes and severity of the condition.
Treatment for Gynaecomastia
Gynaecomastia, a condition characterised by an excess of breast tissue in men, can be addressed through various avenues depending on the severity and underlying causes.
- If you're dealing with mild gynaecomastia that emerges during puberty due to hormonal shifts, your doctor may suggest a wait-and-watch approach. As your hormones settle down, you may find the excess breast tissue reducing on its own.
- For those experiencing discomfort or psychological distress due to persistent gynaecomastia, medication could be a viable path. Your doctor might prescribe hormonal treatments to restore the balance between testosterone and estrogen levels in your body.
- In severe cases where glandular tissue removal is necessary, surgical options may be explored. These could range from liposuction to excision procedures aimed at removing the excess tissue and improving the contour of your chest. While surgery does carry risks such as scarring and potential complications related to anaesthesia, it can provide immediate results that can boost your self-esteem.
Management of Chest Fat
Managing chest fat largely revolves around lifestyle adjustments.
- Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods can promote weight loss. Reducing caloric intake is essential to help shed excess weight.
- Establishing a regular exercise regimen is another critical step. Cardiovascular exercises such as running or cycling paired with strength training exercises targeting upper body muscles like push-ups or bench presses can help sculpt your chest area by reducing body fat and enhancing muscle definition.
It is important to note that addressing chest fat typically relies on your personal commitment to these lifestyle changes. Unlike gynaecomastia treatment, which may call for medical intervention, reducing chest fat is largely in your hands.
The Psychological Impact of Gynaecomastia and Chest Fat
Gynaecomastia and chest fat can have profound effects on an individual's psychological well-being.
- Several men struggle with feelings of embarrassment or low self-esteem due to their physical appearance.
- This emotional burden often leads them to withdraw from social situations or avoid scenarios where their bodies could be exposed, such as at swimming pools or gyms.
Research indicates that nearly 65% of men with gynaecomastia report feeling self-conscious about their condition. It underscores the importance of not only addressing the physical symptoms of these conditions but also the accompanying emotional health concerns.
In conclusion, recognising the differences between gynaecomastia and chest fat is paramount for an accurate diagnosis and subsequent effective treatment. Gynaecomastia, a state triggered by hormonal imbalances causing glandular tissue growth, is distinct from chest fat, which is excess adipose accumulation often linked to lifestyle factors. A correct diagnosis through careful physical examination and medical testing empowers individuals to seek the most suitable treatment options for their unique situations.
Gynaecomastia and chest fat are not merely physical conditions; they also carry significant emotional and psychological dimensions that demand consideration. Thus, it cannot be stressed enough how crucial it is to seek professional advice for comprehensively managing both the physical symptoms and impacts on emotional well-being.
FAQs
- Can gynaecomastia occur at any age?
Yes, gynaecomastia can occur at any age due to hormonal imbalances. It's especially common during puberty but can also affect older men due to declining testosterone levels.
- Can chest exercises help in reducing gynaecomastia?
While chest exercises may help in toning up the muscles and reducing overall body fat, they cannot specifically target glandular tissue growth in gynaecomastia. It is important to consult your family doctor for appropriate treatment options.
- How can I reduce chest fat naturally?
A combination of cardiovascular exercises, strength training, and a balanced diet low in calories can help in reducing chest fat naturally.
- Is gynaecomastia a serious health concern compared to chest fat?
While both conditions can lead to psychological distress due to altered body image, gynaecomastia might indicate underlying hormonal imbalances that need to be addressed.
- Can gynaecomastia be mistaken for chest fat?
Yes, it can be, especially in overweight or obese men. Therefore, it is crucial to get a physical examination done by your family physician if you observe any changes in your chest area.
- Is surgery the only option for treating gynaecomastia?
Surgery is one way of treating gynaecomastia but it is not the only option. Medications that balance hormones may also be effective in some cases.
- Can both gynaecomastia and chest fat occur simultaneously?
Yes, it is possible for someone to have both excess chest fat and gynaecomastia at the same time. In such cases, a combination of weight loss, exercise, and medical or surgical intervention may be necessary.
- Does gynaecomastia result in chest fat?
No, gynaecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue and not the accumulation of chest fat. However, obesity can lead to both chest fat and gynaecomastia in some men.
- Can losing weight help resolve gynaecomastia?
While weight loss can help reduce chest fat, it might not necessarily resolve gynaecomastia. A consultation with your family doctor is advised to understand the best course of treatment.
- What are the first steps to take when uncertain if it is gynaecomastia or chest fat?
It's recommended that you see your family physician at your earliest convenience for a proper diagnosis. It's crucial to understand whether it's hormonal imbalance causing breast tissue growth, or merely the accumulation of excess body fat.