![]() Views: 71
Views: 71
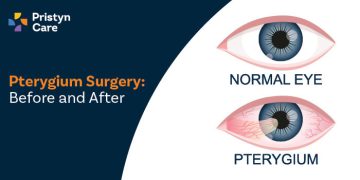
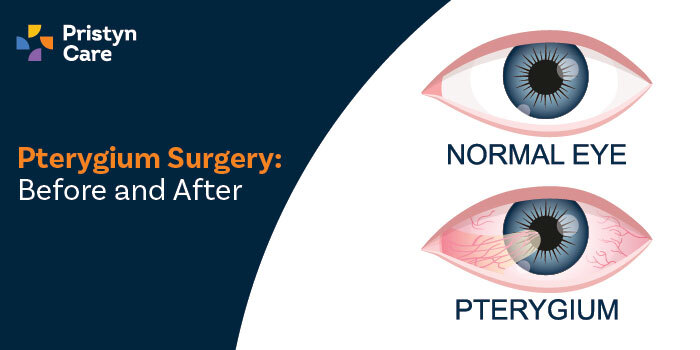
Pterygium Surgery: Before and After
Additionally, we will offer a glimpse into how this procedure can not only improve your appearance but also restore clear vision. .
Dedicated Support at Every Step!
Our Doctors are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week to help you!
Are you dealing with a frustrating growth on your eye? You're not alone. Pterygium, a common eye condition, can significantly affect your vision and appearance but often remains untreated. Fortunately, pterygium surgery offers a proven solution to not only remove this growth but also improve your sight and eye health.
In this post, we will take a close look at what you can expect before and after pterygium surgery. Additionally, we will offer a glimpse into how this procedure can not only improve your appearance but also restore clear vision.
Table of Contents
Pre-Surgery
Preparing for pterygium surgery is critical for both procedure success and patient comfort. This stage involves careful diagnosis, thorough patient counselling, and an overview of the surgical options available.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Accurate diagnosis of pterygium is essential to determine the best surgical approach and adequately prepare the patient for the procedure.
Clinical Examination
The initial step in assessing a pterygium involves a detailed clinical examination by an ophthalmologist. The doctor examines the eye closely to evaluate the following:
- Extent and Location: Checking how far the pterygium extends over the cornea and its exact position.
- Symptoms: Assessing symptoms such as irritation, redness, or blurred vision that the growth might be causing.
- Growth Pattern: Determining whether the pterygium is growing and at what rate. This is crucial for planning the timing of surgery.
Diagnostic Imaging
Additional diagnostic tools may be used to assess the pterygium more precisely:
- High-Resolution Photography: This is used to document the current size and shape of the pterygium for future comparison.
- Corneal Mapping: Technologies like corneal topography provide detailed images of the cornea's surface. These techniques help surgeons understand how the pterygium affects vision and how to remove it.
Patient Counselling and Preparation
Effective communication and preparation are key to make sure that the patient feels secure and informed about the upcoming surgery.
Discussing Potential Risks and Outcomes
Patients must be made aware of what the surgery involves and what to expect in terms of outcomes and potential risks:
- Success Rates: Explaining the effectiveness of the surgery in removing the pterygium and improving symptoms.
- Possible Side Effects: Discussing potential side effects such as discomfort, swelling, or infection.
- Recurrence Possibility: Informing about the likelihood of pterygium recurrence. Recurrence can vary depending on the surgical technique used.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Preoperative Care
Preparing for surgery involves several practical adjustments and precautions:
- Medications: Advising which medications to continue or avoid before the surgery, particularly those that might affect blood clotting.
- Preparations on the Day of Surgery: Instructions on fasting or other preparatory steps required on the day of the surgery.
- Post-Surgery Arrangements: Planning for recovery time, including time off work and the need for assistance at home during the initial recovery period.
Types of Surgical Techniques Overview
Different surgical techniques can be employed to remove a pterygium, each with its own advantages and considerations.
Traditional Surgery
Traditional surgery involves the complete removal of the pterygium tissue from the eye:
- Procedure Details: The surgeon excises the pterygium along with a small part of the surrounding conjunctiva to ensure complete removal.
- Grafting: In some cases, a small graft from another part of the conjunctiva is used to cover the area, reducing the risk of recurrence.
- Recovery: Postoperative care includes using eye drops to manage inflammation and prevent infection, with follow-up visits to monitor healing.
Minimally Invasive Approaches
Advances in surgical techniques have led to the development of less invasive methods with quicker recovery times:
- Sutureless Surgery: Techniques such as fibrin adhesive or autologous blood can be used to attach conjunctival autografts without sutures, reducing irritation and speeding recovery.
- Amniotic Membrane Transplantation: This method involves placing a piece of sterilised human amniotic membrane over the area where the pterygium was removed. This promotes healing and reduces scarring.
- Advantages: These methods generally result in less discomfort post-surgery and a lower chance of the pterygium returning.
No Cost EMI, Hassle-free Insurance Approval
During Surgery
Pterygium surgery is a precise process to remove abnormal tissue from the eye and prevent recurrence. The operation involves specific steps, from preparing the patient to the surgical procedure.
Anaesthesia and Patient Setup
The beginning of pterygium surgery focuses on ensuring the patient's comfort and safety by appropriately administering anaesthesia and carefully positioning the patient.
Choosing the Appropriate Anaesthesia
Selecting the right type of anaesthesia is crucial for the patient's comfort during the procedure. Options include:
- Local anaesthesia: Most commonly used in pterygium surgery, local anaesthesia numbs the eye area while the patient remains awake. This method is safe and effective, allowing for immediate patient feedback during the procedure.
- Sedation: For patients who may feel anxious about being awake, sedation provides a relaxed state but with the patient still conscious.
- General anaesthesia: Rarely required for pterygium surgery, but may be considered if the patient has specific medical conditions or if extensive surgery is planned.
Patient Positioning
Proper positioning is key to the success of the surgery. The patient lies flat on the operating table with their head secured to prevent movement. The eye undergoing surgery is aligned with the surgical microscope, and the area around the eye is cleaned and draped to maintain sterility.
Step-by-Step Surgical Procedure
The surgical procedure for removing a pterygium requires careful execution by the surgeon.
Excision of Pterygium
The surgeon carefully removes the pterygium tissue from the sclera (the white part of the eye) and cornea. This step includes:
- Cutting the Pterygium: Using precise surgical instruments, the surgeon slices at the head of the pterygium to separate it from the cornea.
- Removing the Body: The body of the pterygium is gently peeled away from the underlying tissue so that all abnormal cells are removed to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Grafting Techniques
After the excision, the exposed area may be covered using a grafting technique to promote healing and further reduce recurrence.
- Conjunctival Autograft: Tissue from another part of the patient's conjunctiva (the clear lining of the white part of the eye) is transplanted to the affected area.
- Amniotic Membrane Graft: A sterilised piece of human amniotic membrane may be placed over the area to facilitate new healthy tissue growth and reduce inflammation.
Application of Mitomycin-C
Mitomycin-C, an anti-scarring agent, is sometimes applied to the surgical area to prevent fibrous tissue growth, thereby minimising the chances of pterygium recurrence. This application involves:
- Controlled Exposure: Mitomycin-C is applied for a brief period during surgery under the careful watch of the surgeon.
- Thorough Rinsing: After application, the area is rinsed meticulously to ensure no excess medication remains, which could cause complications.
Intraoperative Care
During the operation, constant monitoring and management are essential to promptly address any issues that may arise.
Monitoring Vital Signs
Throughout the surgery, the patient's vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation) are continuously monitored for stability and immediate response to any physiological changes.
Managing Intraoperative Complications
While complications during pterygium surgery are rare, the surgical team is prepared to manage them. Some complications include:
- Bleeding: Minor bleeding can occur when the pterygium is removed. It is usually controlled with gentle pressure or cauterisation.
- Unexpected Reactions to anaesthesia: Although rare, some patients may react adversely to anaesthesia. In such cases, the anaesthetic team will adjust the anaesthesia or administer medications to counteract these reactions.
Post-Surgery
After pterygium surgery, effective postoperative care is crucial to ensure a smooth recovery and prevent complications. The care regimen is designed to manage pain, prevent infection, and ensure long-term health of the eye.
Immediate Postoperative Care
Immediate care following pterygium surgery focuses on comfort and the prevention of complications. This phase is critical in setting the foundation for a successful recovery.
Monitoring and Managing Pain
Pain management is a priority immediately after surgery. Patients typically experience mild to moderate discomfort, which is managed through:
- Pain Relief Medications: Oral pain relievers are commonly prescribed to manage discomfort during the first few days post-surgery.
- Cool Compresses: Applying cool compresses to the eye area can help reduce swelling and soothe pain.
- Rest: Patients are advised to rest their eyes, avoiding any strain in the initial recovery period.
Infection Prevention
Preventing infection is paramount for a successful recovery. Steps include:
- Antibiotic Eye Drops: These are routinely prescribed post-surgery to prevent bacterial infections.
- Sterile Techniques: Patients are instructed on how to care for the eye in a way that maintains cleanliness and avoids contamination.
- Awareness of Symptoms: Patients are educated on the signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge, which should prompt immediate consultation with their doctor.
Long-Term Outcomes and Follow-up
Long-term care is essential to guarantee the surgery's success and monitor for any signs of recurrence.
Regular Follow-up Visits
Routine postoperative visits are crucial to monitor the healing process and intervene early if issues arise. These visits typically include:
- Initial Check-up: Often scheduled the day after surgery to assess the initial healing.
- Subsequent Reviews: Follow-up appointments are usually planned for the weeks, months, and sometimes a year after surgery to ensure proper recovery and assess any long-term needs.
- Vision Tests: Regular vision assessments to evaluate any changes or improvements in sight.
Identifying and Managing Recurrences
Although rare, pterygium can recur. Monitoring and early management are key to dealing with recurrences:
- Regular Inspections: The eye is examined for any signs of new growth.
- Preventive Measures: Patients may be advised on lifestyle changes or protective measures to minimise the risk of recurrence, such as wearing UV-protective eyewear.
- Treatment Options: If recurrence occurs, options may include further surgical interventions or non-surgical treatments like eye drops or ointments.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehabilitation focuses on ensuring a return to normal activities and lifestyle adjustments post-surgery.
Use of Medications (e.g., Steroids, Antibiotics)
Postoperative medications play a critical role in the recovery and rehabilitation process:
- Steroids: Steroid eye drops are commonly used to reduce inflammation and help the eye heal properly.
- Continued Antibiotic Use: Depending on the doctor’s assessment, antibiotic treatment may continue to prevent postoperative infection.
- Pain Management: Ongoing management of any discomfort through over-the-counter pain relievers as recommended by the surgeon.
Lifestyle and Activity Adjustments
Returning to daily activities must be managed carefully to avoid complications:
- Avoiding Strain: Avoid activities that strain the eyes, such as reading, watching TV, or using a computer, for a short period post-surgery.
- Protective Eyewear: Wear sunglasses to protect the eye from UV rays and debris when outdoors.
- Activity Graduation: Gradually increase normal activities based on the recovery rate and under the guidance of the eye care professional.
Vision Restored: A Closer Look at Beating Pterygium
All in all, pterygium surgery marks a significant transformation for those affected by this eye condition. From initial diagnosis to detailed surgical interventions and thorough postoperative care, each step is designed to maximise patient outcomes and comfort.
Our guide has outlined the essential phases, ensuring you are well-prepared and informed. If you're considering this procedure, remember that ongoing follow-up and adhering to your doctor's advice are key to maintaining your vision and preventing recurrence. Here's to a clearer, brighter future for your eyes.
FAQs
Q1. What is pterygium surgery?
Pterygium surgery involves removing a non-cancerous growth on the eye's conjunctiva. Surgeons often use a graft to cover the area to improve symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Q2. What is the success rate of pterygium surgery?
Pterygium surgery has a high success rate, typically over 90%. It effectively reduces symptoms and prevents the growth from returning.
Q3. What is the cost of pterygium surgery in India?
The cost of pterygium surgery in India varies but generally ranges from ₹15,000 to ₹40,000. Prices depend on the hospital and the specific surgical technique used.
Q4. How many hours is pterygium surgery?
Pterygium surgery usually takes about 30 to 45 minutes. The duration depends on the case's specifics and whether any additional procedures are necessary.