![]() Views: 100
Views: 100
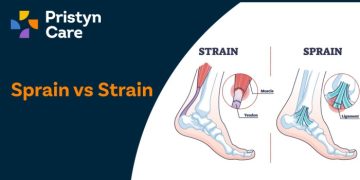
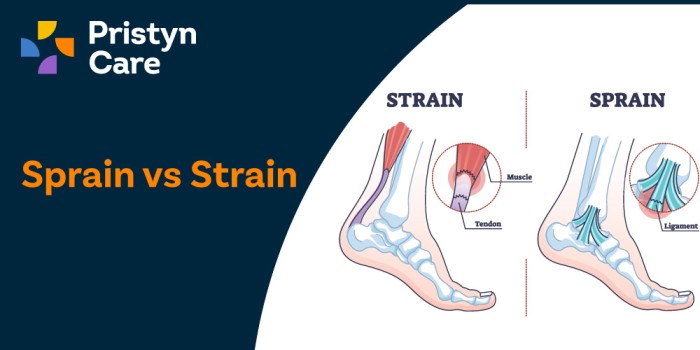
Sprain Vs Strain
You may feel pain after a sudden twist or a sharp pull, but is it a sprain or a strain? Understanding the nuances between these two injuries is crucial for effective treatment and quick recovery.
Dedicated Support at Every Step!
Our Doctors are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week to help you!
This blog gets into the sprain vs strain differences to help you identify which injury you might be dealing with. We'll explore their distinct symptoms, causes, and recommended recovery strategies.
Whether it is a twisted ankle from a jog or a back strain from lifting heavy objects, knowing the right terminology and treatment can significantly influence your healing process. Stay informed and prepared to handle these common injuries with confidence. Let's get started with the essential details that everyone should know.
Table of Contents
Sprain Vs Strain Differences | Overview
Knowing the differences between sprains and strains can help you manage these injuries more effectively. Here is a basic overview of sprain and strain.
Definition of Sprains
A sprain occurs when you stretch or tear the ligaments that connect two bones together in your joints. It often happens when the joint gets twisted while bearing weight, leading to sudden overstretching or tearing of these supporting bands.
Common areas for sprains include ankles, wrists, and knees. The injury can range from mild, involving slight stretching, to severe, involving complete tears.
Definition of Strains
A strain, on the other hand, involves the stretching or tearing of muscles or tendons. Tendons are the tough fibres that connect muscles to bones.
Strains are commonly a result of overexertion or improper use of a muscle. They often occur in the back and the hamstring muscle, which is located at the back of the thigh.
No Cost EMI, Hassle-free Insurance Approval
Symptoms of Sprain and Strain
Here are the symptoms of sprain and strain below:
Common Symptoms of Sprains
Sprains are injuries affecting the ligaments that support and stabilise the joints. The most common symptoms of a sprain include immediate pain at the time of injury, which can vary from mild to severe depending on the extent of the damage. Here are some detailed pointers on the symptoms:
- Pain: The affected area typically hurts immediately after the injury, especially when attempting to use or move the joint.
- Swelling: This is a rapid reaction to the injury, as the body increases fluid in the area to start the healing process.
- Bruising: As ligaments tear, they may bleed internally, causing bruising around the affected joint.
- Limited Mobility: Depending on the severity, you might find it difficult to move the joint normally without pain.
- Sounds at the Time of Injury: Some people hear or feel a pop or snap at the joint when the injury occurs.
Common Symptoms of Strains
Strains affect muscles or tendons and are particularly common in the legs and back. The symptoms can be similar to sprains but are related to muscular rather than joint injuries. Key symptoms include:
- Pain: Muscle pain is present both during rest and especially when the injured muscle is used.
- Swelling: Like sprains, strains can cause swelling, which can make the muscle feel stiff and weak.
- Muscle Spasms: Strained muscles may spasm as they contract painfully and involuntarily.
- Reduced Flexibility: You may notice reduced range of motion in the affected muscle.
- Weakness: The muscle may feel weaker than usual, making it difficult to use as normal.
When to Seek Medical Attention?
It is crucial to know when an injury requires more than just home care. Here are several pointers that indicate it's time to seek medical attention:
- Severe Pain and Swelling: If pain or swelling is severe and becomes unbearable, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider.
- Inability to Support Weight: If the injured area cannot bear weight or you cannot use it without significant pain, professional assessment is necessary.
- Deformity or Unusual Angles: If the joint or muscle looks deformed or is oddly positioned, this may indicate a severe injury requiring immediate medical intervention.
- No Improvement: If symptoms do not improve with home treatment within a few days, it may be necessary to consult a healthcare professional to prevent further damage.
- Recurrent Injuries: Frequent injuries to the same area may require a professional to assess for underlying issues that could be contributing to the problem.
Orthopaedic Care for Sprain vs Strain
Below, we will learn about orthopaedic care for sprain vs strain:
Initial Treatment Options for Sprains and Strains
Initial treatment for both sprains and strains focuses on reducing pain, swelling, and the risk of further injury. The widely recommended approach is the RICE method, which stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Here’s a breakdown of each step:
- Rest: Cease any activities that cause pain to prevent further injury. It's crucial to rest the injured area during the early stages of recovery.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area for 20 minutes every two hours for the first 48 hours. Ice helps reduce swelling and numbs the surrounding tissue to dull pain.
- Compression: Use an elastic bandage to wrap the injured area. This should be snug but not too tight, helping to keep swelling down.
- Elevation: Keep the injured area raised above the level of your heart, especially during the first few days. This helps reduce swelling by draining excess fluid.
Over-the-counter pain relief medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can also be used to manage pain and inflammation.
When to Visit an Orthopaedic Specialist?
While many sprains and strains can be managed at home, there are certain situations where it's advisable to visit an orthopaedic specialist:
- Persistent or Increasing Pain: If pain doesn’t decrease with initial home treatment or worsens, you should see a specialist.
- Limited Mobility: If you experience trouble moving the affected joint or muscle, professional assessment may be needed to rule out severe injury.
- Signs of Severe Injury: Severe swelling, bruising, or signs of deformity can indicate a more serious condition that might require advanced treatments like surgery.
- No Improvement: If there's no improvement after a few days of home treatment, a specialist can assess the need for additional interventions or physical therapy.
Long-Term Care and Rehabilitation
Long-term care and rehabilitation are critical for full recovery and preventing future injuries. Here's what this typically involves:
- Physical Therapy: Once the initial pain and swelling have decreased, physical therapy might be necessary. A therapist will guide you through exercises designed to restore the joint or muscle’s strength and flexibility.
- Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises will help strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected area, supporting recovery and reducing the risk of recurrence.
- Flexibility Training: Stretching exercises are essential to maintain and improve the range of motion of the affected joint or muscle.
- Gradual Return to Activity: It’s important to slowly reintegrate into regular activities as strength and flexibility improve. Rushing this process can lead to setbacks.
- Education and Prevention: Learning proper techniques and warm-up exercises can prevent future sprains and strains. An orthopaedic specialist or physical therapist can provide valuable guidance.
Preventive Measures
Preventing sprains and strains is crucial for maintaining an active, injury-free lifestyle. These injuries can sideline you for weeks or even months. With the right precautions, however, many can be avoided. Here’s how you can keep yourself safe and active.
Tips to Prevent Sprains
Sprains are injuries to ligaments caused by twisting or pulling movements. Here are some tips to help avoid these painful incidents:
- Proper Footwear: Wear shoes that provide good support and are suitable for your activity. For example, hiking boots for rough terrain and sports-specific footwear for activities like basketball or soccer.
- Warm-Up Exercises: Before engaging in any sports or exercise, perform warm-up routines to prepare your joints and ligaments for the activity.
- Increase Flexibility: Regular stretching can increase your joint flexibility, reducing the risk of ligaments being forced beyond their normal range of motion.
- Avoid Uneven Surfaces: When exercising or playing sports, try to stay on even surfaces to reduce the risk of ankle sprains.
- Use Protective Gear: Braces or supportive tapes can be used in high-risk activities or by individuals with a history of sprains.
Tips to Prevent Strains
Strains are injuries to muscles or tendons, often caused by overexertion. Here are effective ways to prevent these injuries:
- Strength Training: Building muscle strength supports joints and reduces the likelihood of muscle overstretching and tearing.
- Proper Technique: Learn the correct technique for your activities. Incorrect movements can overstretch or tear muscles and tendons.
- Regular Breaks: Take breaks during activities to prevent muscle fatigue, which can lead to strains.
- Gradual Increase in Activity: Increase the intensity and duration of your activities gradually. Sudden increases can shock muscles and lead to injuries.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration helps keep muscles supple and less prone to injuries.
Importance of Proper Equipment and Training
Using the right equipment and getting proper training are essential components of preventing sprains and strains.
- Use Appropriate Equipment: Always use the correct equipment for your activities. This includes weights, machines, or protective gear that is the right size and fit for your body.
- Professional Training: If you’re unsure about the correct technique for an exercise or sport, consider getting professional training. A trainer can guide you on how to perform movements correctly, which significantly reduces the risk of injury.
- Maintain Equipment: Regularly check and maintain your sports and exercise equipment to ensure it remains safe to use.
- Educational Workshops: Attend workshops or training sessions on injury prevention in sports or work environments, especially if your activities have high injury risks.
Treatment Options
When you suffer from a sprain or strain, effective treatment is essential to speed up recovery and prevent further injury. The right approach can help reduce pain, restore function, and get you back to your daily activities more quickly.
Home Remedies and First Aid
Initial treatment for sprains and strains often begins at home. The RICE method is the cornerstone of early care:
- Rest: Stop any activities that cause pain. Rest decreases the risk of worsening the injury.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the injured area for 20 minutes every two hours to reduce swelling and numb the pain.
- Compression: Use an elastic compression wrap to decrease swelling. Ensure it’s snug but not too tight, which could impede circulation.
- Elevation: Elevate the injured area above the level of your heart whenever possible, especially during the first 48 hours, to help reduce swelling.
Additional home remedies include:
- Pain Relief Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or paracetamol can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Gentle Stretching: Once the initial pain subsides, gentle stretching can help maintain mobility and prevent stiffness.
Medical Treatments Available
If home remedies are not enough, medical treatments may be necessary, especially for more severe injuries. These treatments include:
- Physical Therapy: A physiotherapist can develop a personalised program to strengthen the injured area and restore range of motion.
- Pain Management: For intense pain, doctors may prescribe stronger medications or recommend therapeutic modalities like heat therapy or electrical stimulation.
- Orthotics and Supports: For ankle sprains or similar injuries, supportive devices like braces or orthotics can stabilise the area and prevent future injuries.
For chronic issues or severe cases, the following medical interventions might be considered:
- Corticosteroid Injections: These can be used for both sprains and strains to reduce severe inflammation.
- Ultrasound Therapy: This technique uses sound waves to promote deep tissue healing and is often used by physical therapists.
Surgical Options if Required
Surgery is usually considered a last resort and is reserved for injuries that do not respond to other treatments or involve significant tissue damage:
- Reconstructive Surgery: For complete tears of ligaments or tendons, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged structures.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure that allows surgeons to view inside the joint and repair any damage with small instruments and incisions.
Post-surgical care includes:
- Rehabilitation: Post-operative rehabilitation is crucial and typically involves a combination of physical therapy and gradual return to activity.
- Follow-up Care: Regular follow-ups with the surgeon or therapist are necessary to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovering from a sprain or strain properly is crucial to avoid long-term issues and regain full mobility. This section will guide you through the expected recovery timelines, beneficial physical therapy exercises, and how to safely return to normal activities.
Recovery Timelines for Sprains and Strains
The recovery time for sprains and strains varies depending on the severity of the injury:
- Mild Sprains and Strains (Grade 1): Typically heal within one to three weeks. These involve minor stretching with no significant tearing.
- Moderate Sprains and Strains (Grade 2): Can take three to six weeks to heal. These injuries may involve partial tearing of the ligaments or muscles and require more careful management to heal properly.
- Severe Sprains and Strains (Grade 3): May take several months to fully heal. These involve complete tears or ruptures and often require surgical intervention followed by extensive rehabilitation.
It’s important to follow medical advice closely throughout your recovery to ensure that the injury heals well and does not recur.
Physical Therapy Exercises
Engaging in physical therapy exercises is essential for effective rehabilitation:
- Flexibility Exercises: These help to restore the range of motion. Gentle stretching should be done only to the point of tension, not pain.
- Strengthening Exercises: As the pain subsides, exercises to strengthen the surrounding muscles will help support the injured area and prevent future injuries.
- Balance and Coordination Exercises: Particularly important for ankle and knee injuries to retrain the senses responsible for the stability of these joints.
A physical therapist will tailor these exercises to your specific injury and recovery stage, ensuring you progress at a safe pace.
Returning to Normal Activities
Returning to your usual activities should be a gradual process:
- Start Slowly: Begin with light activities that do not strain the injured area. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of these activities as your strength and flexibility improve.
- Monitor Pain: Always listen to your body. Pain is a sign that you might be pushing too hard or too fast. Adjust your activity level accordingly.
- Preventive Measures: Continue to use any recommended supports and engage in preventive exercises to avoid future injuries.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of sprains and strains, it's crucial to carry forward the knowledge that can transform mishaps into manageable situations. Both sprains, which target your ligaments, and strains, affecting muscles or tendons, require thoughtful attention to prevent long-term damage.
Here are your quick action points:
- Use RICE as your first response to injury.
- Gradually return to activity with the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Invest in preventive measures to avoid future injuries.
As you move forward, keep this information in mind. It will help you respond effectively to injuries and support your journey back to full health. Whether it's through careful rehabilitation or by adjusting your daily activities, every step is important.
Stay safe, stay active, and remember to listen to your body—it's the best way to avoid setbacks and achieve a speedy recovery.