![]() Views: 29
Views: 29
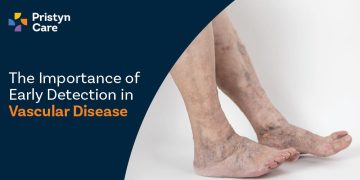
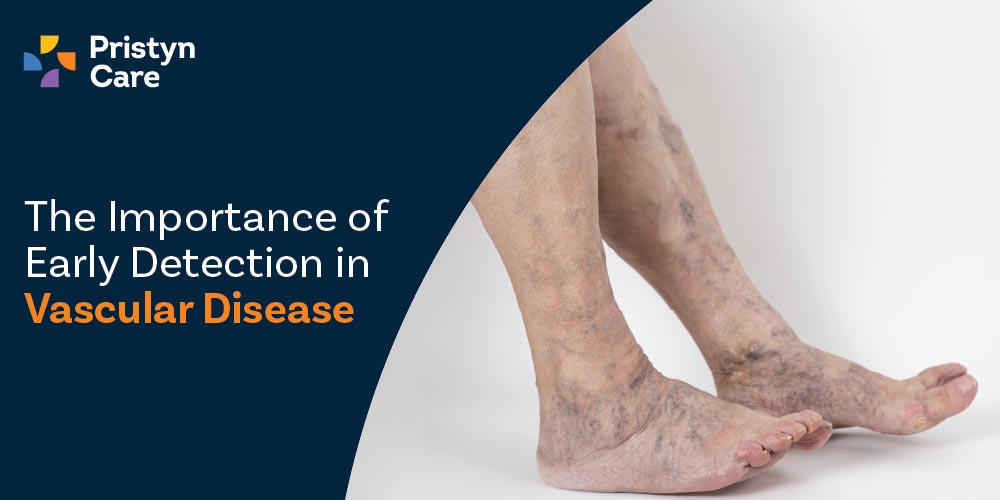
The Importance Of Early Detection In Vascular Disease
Dedicated Support at Every Step!
Our Doctors are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week to help you!
These damaging diseases develop silently over time, with noticeable symptoms frequently absent in the early stages. This lack of symptoms poses a challenge for individuals to identify the problem and seek prompt medical attention.
Consider these facts:
- Vascular diseases can lead to life-threatening complications.
- These diseases often develop without any early symptoms.
- Detecting vascular diseases early can significantly improve the prognosis.
Thanks to advancements in medical technology and growing awareness about this issue, doctors are now more equipped to detect vascular diseases at an earlier stage. This allows for timely intervention and a chance at better patient outcomes.
This article delves into the vital importance of early detection in managing vascular disease. We will explore the immense benefits of early diagnosis and discuss various screening methods available today.
Understanding the significance of early detection empowers you to take proactive steps toward maintaining your vascular health. It also aids in reducing the burden of vascular disease on our healthcare system at large. Not only that, but it also goes a long way towards ensuring a healthier, happier life for yourself.
Table of Contents
Understanding Vascular Disease
Vascular disease is a broad term encompassing several conditions that affect your circulatory system, which includes the arteries, veins, and lymphatic vessels. These conditions can lead to various complications, some of which are:
- Atherosclerosis: This condition represents the buildup of plaque in your arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing your risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): This happens when the arteries in your arms or legs become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow and potentially leading to limb amputation.
- Aortic Aneurysm: This refers to a weakening and bulging of the aorta (the primary artery that carries blood from your heart to the rest of your body), which can lead to life-threatening ruptures if left untreated.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): This is characterised by the formation of blood clots in deep veins, usually in the legs. If the clot breaks off and travels to your lungs, it could lead to pulmonary embolism.
Vascular disease has multiple causes, which can vary depending on the specific type of condition. The primary causes include:
- Atherosclerosis: The most common cause of vascular disease; it involves the buildup of plaque within arteries.
- Genetics: Genetic factors play a significant role in predisposition to vascular diseases.
- Lifestyle Factors: Several lifestyle choices such as obesity, smoking, and physical inactivity significantly contribute to developing vascular disease.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol are associated with an increased risk of vascular disease.
- Other Factors: Infections that cause inflammation of blood vessels known as vasculitis, injuries that damage blood vessels, and some medications like hormone replacement therapy can influence vascular health.
The symptoms of vascular disease can vary depending on the specific type and location of the disease but generally include:
- Pain and discomfort in the limbs during physical activities.
- Skin changes such as coldness, colour changes, and shininess due to reduced blood flow.
- Weakness and numbness in affected areas.
- Non-healing wounds or ulcers, especially on the feet or legs, which indicate poor circulation.
Recognising these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment as untreated vascular disease can lead to serious complications such as heart attacks, strokes, and limb loss. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult your family physician for evaluation and management.
No Cost EMI, Hassle-free Insurance Approval
Importance of Early Detection
The importance of early detection in managing vascular diseases cannot be overstated. Detecting these conditions at an initial stage can have a profound impact on reducing morbidity rates, improving prognosis, and enhancing the quality of life.
Below are some pivotal benefits of early detection in vascular disease:
- Improved treatment outcomes: By identifying and intervening at an early stage, it's possible to slow down or even halt the progression of vascular disease, leading to optimal long-term results for patients.
- Reduced risk of complications: Early detection means that doctors can take necessary measures to prevent or delay serious conditions like heart attacks, strokes, and limb amputations that can occur as complications from untreated vascular diseases.
- Increased treatment options: When vascular disease is found early, patients may find they have a broader range of treatment choices at their disposal – including less invasive procedures and beneficial medications.
- Cost savings: Early discovery and subsequent treatment of vascular disease can result in considerable cost savings for both patients and the healthcare system. It reduces the requirement for complex treatments that can be expensive.
Strategies for Early Detection of Vascular Diseases
To ensure early detection of vascular diseases, consider these strategies:
- Regular Screenings: Routine check-ups play a crucial role in identifying vascular issues before they start showing symptoms. Doctors may recommend tests like blood pressure measurements, cholesterol level checks, and Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) tests that evaluate blood flow in your limbs.
- Understanding Risk Factors: By being mindful of personal risk factors - such as age, family history, obesity, smoking habits, diabetes, and hypertension - individuals can make informed decisions to seek medical advice proactively.
- Recognizing Early Symptoms: Knowledge about early signs of vascular disease like leg pain during activity or changes in skin texture or numbness will help you seek medical consultation promptly. This timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes and minimise the risk of severe complications.
By adopting these strategies into your health management approach, it can help you maintain your vascular health. In the realm of vascular diseases, remember - early detection is the key to safeguarding your well-being.
Clinical Advances in Early Detection
The early detection of vascular diseases is pivotal for successful treatment and control.
Over the years, we have seen significant evolution in diagnostic techniques, ranging from traditional methods to the latest technological breakthroughs. Here, we will explore both these aspects to gain an understanding of how far we've come in identifying vascular diseases at their inception.
Traditional Diagnostic Techniques
- Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI): This is a straightforward non-invasive test where the doctor compares blood pressure readings taken from your ankle and arm. A lower ABI can indicate the presence of peripheral artery disease (PAD) and potentially impaired blood flow.
- Doppler Ultrasound: By using high-frequency sound waves, this technique helps in assessing blood flow and spotting blockages in arteries. It's particularly helpful for evaluating peripheral vascular disease.
- Angiography: This method involves injecting a contrast dye into your blood vessels, subsequently enabling detailed visualisation of any arterial narrowing or blockages through X-ray imaging.
Technological Advancements
In recent times, advancement in technology has significantly boosted our ability to detect vascular diseases early:
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): This non-invasive imaging procedure uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of your blood vessels without the need for contrast dyes. It helps doctors identify any abnormalities within your vessels.
- Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT): This ultrasound technology measures the thickness of your carotid artery walls. It serves as an early warning sign for atherosclerosis (plaque accumulation in arteries) and cardiovascular risk.
- Biomarkers: Emerging research has identified specific biomarkers linked with vascular health, such as inflammatory markers and endothelial function indicators. These biomarkers can provide valuable insights into potential vascular damage even before clinical symptoms appear.
- Composite Scoring Systems: Recent studies have suggested scoring systems that amalgamate multiple non-invasive tests to evaluate cardiovascular risks more comprehensively. These scoring systems integrate various parameters such as arterial elasticity, blood pressure responses and retinal vascular changes to identify individuals who may be at risk of vascular events but are currently asymptomatic.
By carefully weaving together traditional methods with innovative technologies, these advancements in detection techniques enable healthcare providers to identify vascular diseases early. This paves the way for timely interventions, significantly improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of severe complications.
Preventive Measures and Lifelong Management
To prevent vascular disease and manage it effectively post-detection, one needs to adopt a proactive stance prioritising lifestyle adjustments and regular medical care. Let's look at some essential preventive procedures and tactics for lifelong management:
- Healthy Diet: Adopt a heart-friendly diet to help prevent and control vascular disease. This should include:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Opt for colourful fruits and veggies rich in antioxidants and fibre.
- Whole Grains: Add whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread to your diet for better cholesterol management.
- Lean Proteins: Include lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, legumes, nuts while restricting red and processed meats.
- Healthy Fats: Choose unsaturated fats found in olive oil, avocados, fatty fish, and limit intake of saturated and trans fats.
- Regular Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps in better circulation, maintaining a healthy weight, and reducing blood pressure. Try to include at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week such as brisk walking, swimming or cycling along with strength training exercises twice-a-week.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial as it can significantly lower the risk of vascular disease by preventing damage to blood vessels and slowing down atherosclerosis. Support programmes, medication, counselling can all assist in this endeavour.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Regular visits to your doctor are essential for keeping track of blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar. Early detection enables prompt intervention through medications or lifestyle changes.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can adversely affect vascular health. Techniques such as mindfulness practices, yoga, meditation can be effective in managing stress levels.
- Medication Adherence: For those diagnosed with vascular disease, it is vital to stick to prescribed medications which may include antiplatelet agents, statins or antihypertensives to manage risk factors and prevent further complications.
By incorporating these preventive measures and lifestyle changes, individuals can considerably lower their risk of developing vascular disease, and effectively manage existing conditions. This leads to improved overall health and a better quality of life.
In rounding up, we've seen that while vascular disease can pose serious health risks, early detection offers us a lifeline, helping to manage the condition and prevent severe complications.
We've also touched upon the leaps in diagnostic techniques – from the ankle-brachial index, used traditionally, to the latest innovations like magnetic resonance angiography and biomarker analysis. Such advancements are not just game-changers in terms of early detection of vascular diseases but also enable doctors to identify individuals at risk before they fall into the grip of serious complications.
As we draw this discussion to a close, let's remind ourselves: It's time to take control of our vascular health. Regular visits to your family doctor, tweaks in our lifestyle, and an understanding of our personal health risks can make an enormous difference.
By putting early detection and proactive healthcare at the top of your agenda, you're not just improving your quality of life but also reducing the burden of vascular disease. Remember, when it comes to your health—you hold the power. So why wait? Take that first step today!
FAQs
1. Are there risk factors that can make one more prone to vascular disease?
Yes, factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, high cholesterol levels, and a family history of vascular diseases can increase your risk.
2. Can I prevent vascular disease?
While you cannot control all risk factors for vascular disease, many can be managed through lifestyle changes like adopting a healthy diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and controlling your blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
3. How is vascular disease diagnosed?
Doctors often use several tests to diagnose vascular diseases including physical examinations, blood tests, Doppler ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs.
4. What treatment options are available for vascular disease?
Treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the vascular disease. They range from lifestyle changes and medications to surgical procedures in severe cases.
5. Is it possible to live a normal life with vascular disease?
Certainly! People with vascular diseases can lead normal lives with proper management and treatment. Regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial for effective management of the condition.
6. Can vascular disease lead to other complications?
Yes, untreated vascular disease can lead to serious complications like stroke, heart attack, or even amputation in severe cases.