![]() Views: 268
Views: 268
What is Male Pattern Hair Loss or Baldness? How Can It Be Treated?
Almost 85% of men experience some sort of hair loss problem during their lifetime due to several reasons. And in 95% of cases in males, hair loss can be attributed to male pattern baldness, also called androgenetic alopecia.
Dedicated Support at Every Step!
Our Doctors are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week to help you!
Male pattern baldness presents itself as a receding front hairline or loss of hair on the crown area of the scalp. Once the hair loss begins, men start to feel self-conscious. While some tend to let the hair shedding continue, others take immediate action and try various measures to address hair fall and thinning.
In this blog, we are going to learn about Male Pattern Baldness in detail to gain a better understanding of the causes and effective measures that can be taken to treat and prevent hair loss. Let’s begin by understanding the condition.
Table of Contents
Understanding Male Pattern Baldness
The onset of male pattern baldness typically begins at the age of 35 in males, but early onset is also becoming very common nowadays. The progression is gradual and can occur over several years and may even take decades. The primary factor that contributes to this type of hair loss is genetics and hormones.
Scientists believe that genetic factors affect hair follicles and make them vulnerable to a hormone called DHT (Dihydrotestosterone), which is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone. The genetic sensitivity caused by DHT results in shrinkage of the hair follicles. As the hair follicles become smaller, their life span is also affected, and ultimately, they stop producing hair earlier than usual.
Male pattern baldness exhibits a predictable pattern in most cases. The first pattern is hair thinning, starting on the top of the head and moving around the temples, creating a horseshoe mark. And the second pattern is a recession from the front and pushing the hairline further back on the head. The degree and progression of hair loss in men are assessed through the Hamilton-Norwood Scale, which lists the stages of baldness.
No Cost EMI, Hassle-free Insurance Approval
Various male pattern baldness stages are given below:
- Stage 1: Little or no hairline recession with no noticeable hair thinning.
- Stage 2: Noticeable hair thinning and mild hairline recession around the ears and forehead.
- Stage 3: Deep hairline recession around the temples, and the hairline takes an “M” or “U” shape.
- Stage 4: Hairline recession continues, and the crown or top of the head also starts to lose hair.
- Stage 5: The frontal hairline recession and the crown recession create two bald spots.
- Stage 6: The hair between the crown and temple is gone completely, and these two areas combine.
- Stage 7: Only a band of hair remains on the scalp on the back side and above the ears. These hairs may not also be sparse or fine.
People of Asian descent are more affected by male pattern baldness. And if one of your parents, grandparents, or other family members has the same condition, your odds of losing hair are higher.
Causes of Male Pattern Baldness
As mentioned above, male pattern baldness is caused primarily due to a combination of genetic and hormonal factors. These two components can be affected by various other factors. Let’s understand these factors in detail:
- Genetic Predisposition: The primary cause of male pattern hair loss is believed to be genetic inheritance. It is often passed down through family members, with a specific gene called the androgen receptor (AR) gene playing a significant role. This gene is responsible for regulating hair follicle sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone and responsible for maintaining hair growth throughout the body.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormones, particularly DHT, play a crucial role in the development of male pattern hair loss. In individuals with a genetic predisposition, DHT can bind to receptors in the hair follicles on the scalp. This binding process leads to a gradual shrinking of the hair follicles, shortening their growth cycle and producing progressively finer and shorter hairs. Over time, the affected hair follicles may stop producing new hairs altogether, resulting in baldness.
- Androgen Sensitivity: Hair follicles in the scalp of individuals with male pattern hair loss are genetically more sensitive to the effects of DHT. This increased sensitivity causes the hair follicles to undergo a process called miniaturization, which leads to thinner, weaker, and shorter hairs. Eventually, the miniaturized hair follicles can no longer sustain hair growth.
- Age: Male pattern hair loss typically becomes more noticeable with age, although it can start at any time after puberty. The exact age of onset and the rate of hair loss can vary from person to person, depending on genetic factors and individual variations in hormone levels.
While genetic and hormonal factors are the primary causes of male pattern hair loss, other factors can contribute to its onset or exacerbate the condition. These include:
- Medications: Certain medications, such as some types of chemotherapy drugs, anticoagulants, beta-blockers, and steroids, can contribute to hair loss or accelerate the process in individuals already predisposed to male pattern baldness.
- Chronic Illnesses: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and scalp infections, can cause or exacerbate hair loss.
- Lifestyle and Health Factors: Poor nutrition, smoking, excessive stress, and hormonal imbalances can contribute to hair loss and affect the severity of male pattern baldness.
While it is not currently possible to prevent or reverse male pattern hair loss completely, various treatment options can help slow down the progression of hair loss and promote hair regrowth in some individuals.
Options for Male Pattern Baldness Treatment
There are several treatment options available for male pattern hair loss. The effectiveness of each treatment can vary from person to person, and the suitable option should be chosen after consulting a specialist.
Here are some commonly used treatment options:
- Medications: Minoxidil and finasteride are two medications that are commonly used to address hair loss. Minoxidil is an over-the-counter topical medication that is applied directly on the scalp and helps to prolong the hair growth cycle. Finasteride is a prescription medication taken orally in tablet form. It works by reducing the production of DHT, the hormone responsible for hair loss. Both these medicines should be taken with medical supervision.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): LLLT involves the use of specialized devices, such as laser combs or helmets, that emit low-level laser light onto the scalp. This therapy is thought to stimulate hair follicles, improve blood flow, and promote hair growth. LLLT is available as both in-office treatments and handheld devices for home use.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Commonly known as hair PRP therapy, this treatment method involves extracting a small amount of the patient's blood, processing it to concentrate platelets, and injecting the platelet-rich plasma into the scalp. Platelets contain growth factors that may stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. An advanced form of treatment is also available, called GFC therapy, in which growth factors concentrates are further extracted from the platelets and administered directly on the scalp to promote hair growth.
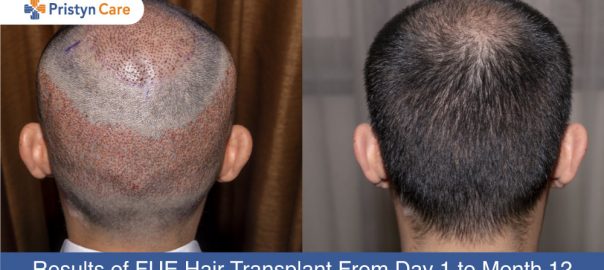
- Hair Transplant Surgery: Hair transplant surgery is a more invasive option that involves taking hair follicles from areas of the scalp resistant to DHT (typically the back and sides) and transplanting them to the balding areas. This procedure can provide long-lasting and natural-looking results, but it requires careful consideration and consultation with a qualified surgeon.
Besides these techniques, there are other options, such as scalp micro pigmentation (injecting hair-colored pigments to replicate the appearance of hair) and camouflage techniques, such as hair sprays, hair fibers, scalp concealers, etc., to conceal the thinning areas. You should also know that each of the above-discussed techniques to treat male pattern baldness has its limitations, and the results vary for each individual.
How to Prevent Male Pattern Baldness?
Preventing male pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia) entirely may not be possible, as it is primarily influenced by genetic and hormonal factors. However, certain measures can help slow down the progression of hair loss or maintain the health of existing hair. Here are some tips that you can try:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Ensure your diet includes a variety of nutrients, including proteins, vitamins (particularly vitamin D and vitamin E), minerals (such as iron and zinc), and omega-3 fatty acids. A well-balanced diet can support overall hair health.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity promotes good blood circulation, including to the scalp, which may help maintain healthy hair.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss. Adopt stress-management techniques such as exercise, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies and activities that help you relax.
- Avoid Overstyling: Excessive heat styling, tight hairstyles, and harsh chemical treatments can damage hair and potentially contribute to hair loss. Minimize the use of heated styling tools and opt for gentle styling techniques.
- Be Gentle While Brushing and Washing: Avoid aggressive brushing or combing, especially when the hair is wet and more prone to breakage. Use a wide-toothed comb or a brush with soft bristles. Be gentle while washing your hair, and avoid vigorous rubbing.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can have a negative impact on hair health and may contribute to hair loss. Quitting smoking or avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke will improve overall hair health by maintaining proper blood circulation and keeping the hair follicles healthy.
It's important to note that while these measures may help slow down the progression of male pattern hair loss or maintain existing hair, they may not prevent it entirely. If you are experiencing significant hair loss or are concerned about your hair, it's advisable to consult a hair specialist.
Pristyn Care Provides Advanced Treatment for Male Pattern Hair Loss
If you’ve been stressed about hair loss and want to do something about it, get in touch with Pristyn Care and consult our expert dermatologists and hair specialists. Our doctors are well-trained in traditional and modern techniques, which have been known to be effective in controlling, managing, and treating hair loss in males.
You can have a detailed consultation with our hair specialist and determine which is the best treatment method for male pattern baldness.