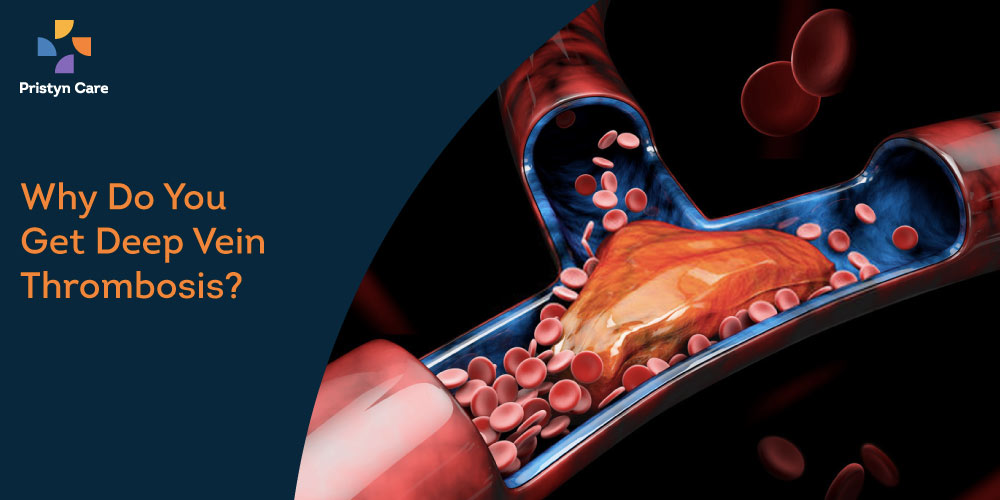
Blood clots that form in deeper veins are dangerous and lead to a condition called Deep Vein Thrombosis. The clots can form in the major veins of the leg, arms, pelvis, or any other part of the body. In some cases, a clot can detach from its point of origin and may travel through the heart to the lungs where it affects the blood flow and leads to pulmonary embolism (an extremely dangerous and fatal condition).
Normally, when you get a cut or scrape, blood clotting helps to stop the bleeding. Also known as coagulation, blood clotting is an important process that helps to prevent excessive bleeding whenever a blood vessel is damaged. Normally, the blood clots are automatically dissolved by the body after the injury heals. However, sometimes, clots can also form inside the vessels without any injury and may not dissolve themselves.
Clots can occur in both veins and arteries. While arteries supply blood from the heart to other organs, veins supply deoxygenated blood to the heart. It means that a blood clot that forms inside the veins can travel to the heart and other organs and may prove life-threatening.
Today, with this blog, you will learn why people get Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and what are its signs and symptoms so that you can identify the problem at the right time and get timely treatment.
Table of Contents
Causes of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Typically, anyone can develop DVT. However, some people are more at risk of developing this condition due to some specific reasons. So, here are the key reasons why people get deep vein thrombosis-
1: Vein Injury
Injuries like breaking a bone or severe damage to the muscles affect the blood vessels too. When the vein is damaged, it disrupts the blood flow and leads to the pooling of blood due to which clots may start to form. Sometimes, major surgeries can also injure the vein and lead to DVT.
2: Lack of Mobility or Physical Activities
Keeping the legs still for a long time can significantly affect the blood flow. Whether you are avoiding moving your legs while recovering from surgery or after a long flight or car ride, immobility will prevent the anti-clotting agents in the body from mixing properly with the blood. This will ultimately lead to blood clot formation, especially in the legs.
3: Hormonal Changes or Medications
Hormonal changes are a primary reason for women to get deep vein thrombosis. The hormones can become imbalanced, especially in women who are on birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy (HRT). It happens due to the artificial estrogen hormone that causes blood to clot at a higher rate.
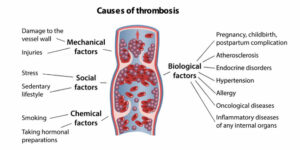
4: Pregnancy
Pregnancy also increases the risk of women developing DVT and keeps on increasing as the week progresses. The body increases the amount of estrogen production to prevent excessive blood loss during childbirth. However, this also puts women at higher risk of DVT.
Also Read: Deep Vein Thrombosis in Pregnancy & Symptoms, Risks, and Treatment
5: Medical Conditions
Some chronic health conditions, such as heart diseases, lung diseases, or inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis are also primary causes of DVT. People who have clotting disorders are also likely to get deep vein thrombosis at some point in life.
6: Obesity/Overweight and Age
With age, it becomes harder to maintain a healthy weight and people often get obese. Age and obesity both make the blood vessels weaker and the physical activities during old age are also reduced. All these things combined put a person at risk of getting DVT.
7: Cancer
When cancer forms, it leads to clotting reactions that make a person more susceptible to DVT. It can happen with any kind of cancer, but most cases are found in people who had cancer in the abdomen and pelvis.
Apart from the above-mentioned causes, a person can also get deep vein thrombosis if he/she has a history of venous diseases, inherited clotting disorder, or takes certain medications that cause coagulation. Regardless of the cause, DVT is a condition that should not be left untreated.
What are the Warning Signs of Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis is a life-threatening condition, and hence it is crucial that you are aware of the signs and symptoms of DVT to get early treatment.
The common symptoms are-
- Swelling and pain in the leg
- Red or discolored skin
- Feeling of warmth in the legs
In many cases, deep vein thrombosis symptoms may not be present until the condition gets severe. Once the clot travels through the heart and reaches the lungs, the following warning signs may appear and you may need emergency help-
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Dizziness, fainting, or feeling lightheaded
- Rapid breathing or pulse
- Coughing up blood
Read More: How To Tell If You Have A Blood Clot In Your Leg?- Warning Signs And Remedies
Consult a Reliable Vascular Surgeon for Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment
Left untreated, DVT can lead to pulmonary embolism and potential death. Therefore, consulting a doctor is very important.
A vascular surgeon is the “Go-To” person for deep vein thrombosis diagnosis and treatment. You can contact Pristyn Care and consult our highly experienced vascular surgeons to resolve the condition. The doctor will identify the cause and provide deep vein thrombosis management tips in the earlier stage. However, if the condition is becoming worse day by day, you may need surgical treatment to remove the blood clots safely and to prevent them from entering the heart or lungs.
Book a free appointment with Pristyn Care and get help from the best vascular surgeons to discuss the treatment options for deep vein thrombosis (DVT).







