
Select City
Hypermature cataract is a severe form of cataract that significantly impairs vision by causing the lens of the eye to harden and cloud extensively. While this advanced stage can lead to serious complications like phacolytic glaucoma, timely surgical intervention can restore clear vision. If you notice symptoms of hypermature cataracts, contact Pristyn Care and consult with the best ophthalmologists for precise cataract surgery. Book your appointment with the nearest eye specialist today
Hypermature cataract is a severe form of cataract that significantly impairs vision by ... Read More




Free Cab Facility

No-Cost EMI

Support in Insurance Claim

1-day Hospitalization

USFDA-Approved Procedure
Choose Your City
It help us to find the best doctors near you.
Bangalore
Chennai
Delhi
Hyderabad
Mumbai
Noida
Pune
Delhi
Hyderabad
Pune
Mumbai
Bangalore
A hypermature cataract, also referred to as a Morgagnian cataract, represents an advanced stage of cataract progression where the eye’s lens becomes excessively hardened and clouded. This condition arises after an initial immature phase and a subsequent mature stage of cataract development. The defining feature of a hypermature cataract is a significant thickening and opacification of the lens, which leads to severe visual impairment.
The lens proteins in a hypermature cataract undergo extensive denaturation and aggregation, which results in the lens appearing whitish or yellowish and becoming densely opaque. Consequently, this impedes the passage of light, severely affecting the clarity of vision and mimicking the effect of looking through a fogged window.
This advanced cataract stage is especially prone to causing complications like phacolytic glaucoma, where escaped lens proteins increase eye pressure, necessitating prompt medical intervention.
The condition is more prevalent among populations with limited access to eye care services and among individuals who delay necessary cataract surgery. The primary treatment involves the surgical removal of the cloudy lens, which is then replaced with an artificial intraocular lens to restore clear vision.

Fill details to get actual cost
Hypermature cataracts develop due to a variety of factors that contribute to the degeneration of the eye’s lens over time. The causes & complications have their mechanisms and risk factors:

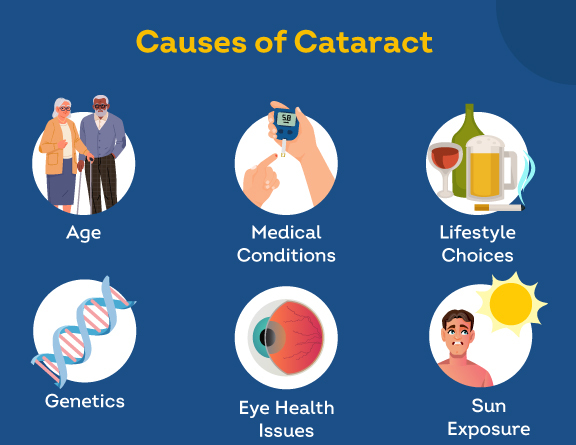
Hypermature cataracts can present in various forms, each with its characteristics:
The symptoms of hypermature cataracts are typically severe and progress as follows:
Diet & Lifestyle Consultation
Post-Surgery Free Follow-Up
Free Cab Facility

24*7 Patient Support
Diagnosing hypermature cataracts involves a series of evaluations that confirm the presence and assess the severity of the cataract. Each diagnostic tool plays a crucial role in planning the appropriate treatment:
Treatment for hypermature cataracts primarily involves surgical intervention, as the lens’s opacity cannot be reversed with medication or corrective eyewear. The standard procedure is:
While all cataracts can affect vision, hypermature cataracts are particularly serious due to their potential to cause severe vision loss and other complications.
While it’s difficult to completely prevent cataracts, particularly those due to aging, certain measures can reduce the risk and delay their progression:
Here are a few myths and facts about hypermature cataract:
Fact: Cataracts do not spread between eyes. They develop independently but can appear in both eyes at different rates.
If you notice any signs of vision impairment such as blurry vision, difficulty seeing at night, or colours appearing faded, it’s important to consult an ophthalmologist. An ophthalmologist specialises in eye health, including the diagnosis and treatment of cataract conditions.
Consulting a specialist is crucial as they can provide a comprehensive evaluation of eye health and determine the appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications such as phacolytic glaucoma and significantly improve the quality of life.
When consulting with your doctor about hypermature cataracts, it’s essential to ask questions that cover both the condition and its treatment:
These questions can help ensure you are fully informed about your condition and the treatment options available, helping you make educated decisions about your eye health.
The main causes include ageing, UV radiation, diabetes, certain medications, smoking, nutritional deficiencies, physical trauma, radiation exposure, and genetic factors. Each of these factors contributes to the degradation of the lens proteins, accelerating the opacity and hardening process.
Types include Intumescent, which involves lens swelling; Morgagnian, where the lens cortex liquefies; Sclerotic, where the lens hardens completely; and Capsular Bag Distension, leading to possible lens dislocation. Each type presents unique challenges and risks for vision and requires specific surgical approaches.
The primary treatment is surgical removal of the clouded lens, replaced with an artificial intraocular lens. Techniques like phacoemulsification are commonly used for effective results. Post-surgery, patients usually experience a significant improvement in vision, often within days.
Yes, a diet lacking in antioxidants like vitamins C and E can accelerate cataract progression, while a nutrient-rich diet might slow it down. Consuming foods high in these antioxidants can help maintain lens clarity for a longer period.
While completely preventing cataracts may not be possible, protecting eyes from UV rays, managing health conditions, and avoiding smoking can reduce risk and delay progression. Regular eye exams also play a crucial role in early detection and management.
Untreated hypermature cataracts can lead to phacolytic glaucoma, lens-induced uveitis, and decreased surgical success due to advanced cataract density. These complications can result in permanent vision loss if not addressed promptly.
Early treatment prevents complications like glaucoma and ensures better surgical outcomes and quicker recovery of vision. Early intervention also helps maintain a higher quality of life by restoring vision clarity sooner.
No, once a cataract is surgically removed and the lens is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens, the specific cataract cannot recur. However, other eye conditions can still arise, and regular eye care remains essential to monitor and maintain overall eye health.
Nusrath Ali
Recommends
Dr meeting was excellent...she has done excellent job means surgery
shailesh sharma
Recommends
She has a wonderful behaviour and listens to patients' problems very carefully. She then offers her opinion. She is very experienced.
Jasmin Naidu
Recommends
Dr Chanchal is amazing with her work truly would recommended to visit & Prystyn management is supportive .
Rajnath Vishwakarma, 77 Yrs
Recommends
Got cataract surgery done for my papa last week. Doctor was really kind and explained everything properly, so giving 4 stars to him. The surgery went fine but papa had some blurriness for 4–5 days after, which made us a bit tensed. It’s better now but we were expecting slightly faster recovery. Overall okay experience but thankful it’s sorted.
.svg)
.svg)